Notes
1. Chemistry Series chapter 1: Periodic Table
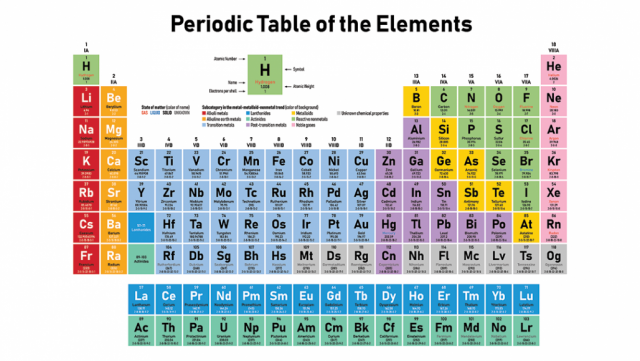
What is Periodic Table?
The arrangement of all the known according to their properties in such a way that the elements of similer properties are grouped together in a tabular form is called periodic table.
History of Development of periodic table:
1] Dobereiner Triad Rule [1817]:
Dobereiner made groups of three elements having similar chemical properties called TRIAD.
In Dobereiner tried, atomic weight of middle element is equal to the average atomic weight of first and third element.
Drawbacks:
But he identify only three triads.
All the known elements could not be arranged in the form of triads.
For very low mass or for very high mass elements, the law was not holding good.
Example:
Cl - 35.5
Br - 80.5
I - 127
(35.5+127) /2 = 81.2
other examples: [K, Rb, Cs], [P, As, Sb], [S, Se, Te], [H, F, Cl], [Sc, Y, La]
2]Newland Octave Rule [1865]:
J.A.R. Nawland arranged the elements in the increasing order of their atomic mass and observe that properties of every 8th element was similar to the 1st one. like in the case of musical vowels notation.
Sa Re Ga Ma Pa Dha Ne Sa
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
At that time inert gases were not known.
The properties Li are similar to 8th element. i.e. Na is similar to Mg.
Drawbacks:
a] This rule is valid only up to Ca. because after Ca due to presence of d-block element there is difference of 18 elements instead of 8 element.
b] After the discovery of Inert gas and included in the periodic table it becomes the 8th element from Alkali metal so this law had to be dropped out.
c] He failed in the case of heavier metals as Fe has been placed atoms with O and S.
3] LOTHER MEYER'S CURVE [1869]
(a) Most electropositive elements i.e. alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs etc.) occupy the peak positions on the curve.
(b) Less electropositive i.e. alkaline earth metal (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba) occupy the descending position of the curve.
(c) Metalloids (B, Se, As, Te, At etc.) and transition metals occupy bottom part of the curve.
4] Mendeleev's Periodic Law
Mendeleev's Periodic Law - The physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic function of their atomic wt.
Characteristic of Mendeleev's Periodic Table -
(a) It is based on atomic wt.
(b) 63 elements were known, noble gases were not discovered.
(c) He was the first scientist to classify the elements in a systematic manner i.e. in horizontal rows and in vertical columns.
(d) Horizontal rows are called periods and there were 7 periods in mendeleev's Periodic table.
(e) Vertical columns are called groups and there were 8 groups in mendeleev's Periodic table.
(f) Each group up to VIIth is divided into A & B subgroups. "A' sub groups element are called normal elements and sub groups elements are called transition elements.
(g) The VIIIth group was consists of 9 elements in three rows (Transitional metals group).
(h) The elements belonging to same group exhibit similar properties.
5] Modern periodic table
It was proposed by Moseley.
Modern periodic table is based on atomic number.
Moseley did an experiment in which he bombarded high speed electron on different metal surfaces and obtained X-rays.
He found out that √v directly proportions to Z where v= frequency of X-rays.
from this experiment, Moseley concluded that the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic number. It means that when the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number elements having similar properties gets repeated after a regular interval. This is also known as 'Modern Periodic Law'.
Modern Periodic Law - The physical & chemical properties of elements are a periodic function of the atomic number.
Characteristics of Modern Periodic Table -
(a) 9 vertical columns called groups.
(b) Ith to VIII group +0 group of inert gases.
(c) Inert gases were introduced in periodic table by Ramsay.
(d) 7 horizontal series called periods.
2. Chemistry Series chapter 2: Structure of Atom
Structure of atom
Basic Details:(a) The word atom was first introduced by Ostwald (1803-1807) in the scientific world.
(b) According to him matter is ultimately made up of extremely small indivisible particles called atoms.
(c) It takes part in chemical reactions.
(d) Atom is neither created nor destroyed.
Basic Definitions:
Electron: It is a fundamental particle of an atom with one unit of negative charge (1.6022 x 10-19 coulomb) and negligible mass (9.10939 × 10-31 kg)
Proton: It is a fundamental particle of an atom with one unit of positive charge (+ 1.6022 x 10-19 coulomb) and a unit mass (1.67262 x 10-27 kg).
Neutron: It is a fundamental particle of an atom with no charge and a unit mass (1.67493 x 10-27 kg).
Nucleus: The small, positively charged dense mass (diameter 10-15 m) present in the center of the atom is called the nucleus.
Extranuclear part: The space around the nucleus, having electrons, is called the extranuclear part.
Atomic number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called its atomic number (Z).
Mass number: The total number of nucleons (protons and neutrons) in the nucleus of an atom is called mass number (A).
Isotopes: They are the different atoms of the same element having the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Isobars: They are the atoms of the different elements having the same mass number but different atomic numbers.
Isotones: They are the atoms of the different elements having the same number of neutrons.
Wavelength: It is the distance between the two nearest crests or troughs (2).Frequency: It is the number of waves that pass through a given point per second (v).
Velocity : It is the distance travelled by a wave in one second (v or c). Also v = v 1.
In next part we will see all Theorems and Experiments of atomic structure.
.png)





![Organic Chemistry Concepts [A-Z] in just 1 Hour | GOC | PLAY Chemistry](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/nP0gDV0xDLY/mqdefault.jpg)












.jpg)
.png)





 संज्ञा
संज्ञा  The Living World
The Living World